Instrument for Measuring Torsional Properties of Fibers and Yarns
Introduction
Textile fibers and yarns are subjected to torsional strains during various processes of manufacture. Such strains affect snarling, unwinding, knittability, etc. during processing and spirality, shape factor, dimensions of loop in knitted products and drape, crease recovery, crepe effect, etc in woven fabrics. It is therefore essential to test and characterize the torsional properties for achieving better production and quality. Keeping this in view, an instrument 'TORSIOMETER' has been designed and developed by Dept. of Textiles Technology, IIT, Delhi. It works on the principle of torsion balance. Presently there are no instruments available for measurement of torsional properties of fibres and yarns
A schematic diagram of the instrument is given at Figure 1. The instrument is supported by circular plates (P1, P2, P3, P4 &P5) and 3 vertical rods. Torsion element (TW) with a known torque factor is selected according to the material to be tested is secured between Jaws (J1&J2) and the gauge length adjusted by Adopters (AD1,AD2). Similarly the test specimen (S) is secured between jaws (J3 & J4) with the required gauge length. Test parameters like direction of rotation, number of rotation, speed, tension, sample particulars are selected from user friendly software and the stepper motor (M) is started. The rotational movement of the motor is transferred to torsion element, Encoder (EN) and the test sample while the bottom jaw (J4) is kept stationary. This introduces twist in the sample which in turn is transferred to torsional element. The twist (torsional force) so introduced results in the speed of the lower end of torsional element to lag behind the speed of stepper motor. Depending on the sample material and the torsional force introduced in it, tension in the sample changes. To maintain the tension constant load cell (LC) and Solenoid (SL) are used. The load cell senses the change in the tension (caused by the change in length of test sample) and send signals to the microprocessors for supplying voltage to the solenoid. Depending on the voltage supply, the core in the solenoid moves suitably for maintaining the tension in the sample constant. During this process the signals received from the encoder are converted to data in digital form. These data recorded at selected intervals are processed to obtain the desired test results. 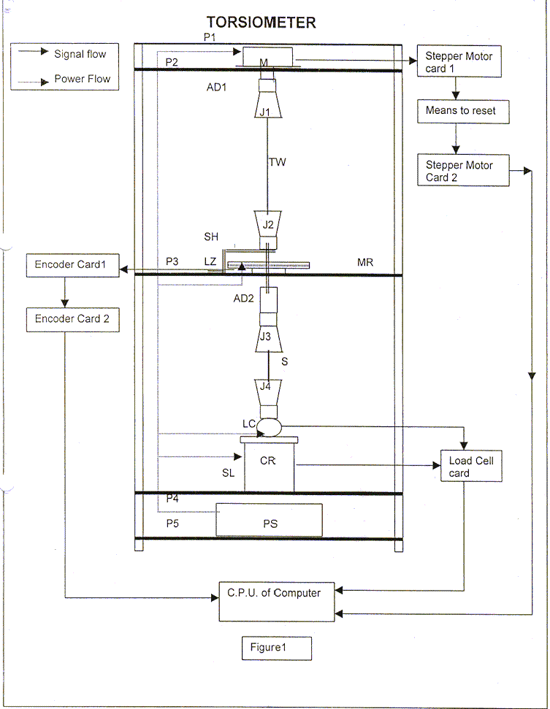
Special Features
A microprocessor controlled stepper motor to introduce required twist in required direction at specified speed in the sample Axially balanced holding jaws for test sample and torsion element Torsion element for measuring the torque in test sample Very sensitive electronic system (encoder) for measuring the twist inserted in the test sample and recorded by interfacing with computer. A solenoid for applying and maintaining required tension in the test sample during testing. A strain gauge for measuring and controlling tension in the test sample User friendly system by the use of suitable microprocessors and computer programming for selection of testing conditions and recording as also processing of data
Prospective Users
The instrument is useful to all those who are concerned with torsional properties of fibers, yarns, tapes, twines, etc. Spinners of spun yarns can find out the residual torque to understand the twist setting or conditioning or snarling tendency of yarn. Fabric manufacturers can assess yarn performance for functional properties like drape, creep or crease recovery. Weaver or yarn consumer can determine unwinding behavior or rolling tendency of yarn during the process. Knitter can assess knittability of yarn or quality of his product with respect to loop dimensions, loop shape and spirality. Texturing processor can assess the quality of the yarn by testing residual torque, one of the important factors of quality checking of yarn after texturising. In case of plied yarns balance of twist is an important factor for better functioning of yarn.The characterization of fibers to understand its response to dynamic twisting is concern of all spinners because the torsional rigidity of fibers influences migration of fibers.
Keywords
Torsion, Fiber, Yarn
Type of Technology
Product together with Software
Status of IPR Protection
Indian Patent Application No 769/DEL/2002 dated 24.7.2002 entitled "An Instrument for Measuring Torsional Properties of Fibers and Yarns"
For further information please contact
Managing Director
Foundation for Innovation and Technology Transfer (FITT)
Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
Hauz Khas, New Delhi-110016, INDIA
Tel : 91-011-26597167, 26857762, 26581013, 26597153
Fax : 91-011-26851169
E-mail : drkdpn@gmail.com







