Fuel Pellets from Municipal Waste
Introduction
In about a decade, major Indian cities such as Delhi, Mumbai, Calcutta will find difficult to dump its daily garbage of more than 5,000 TPD. The existing dumping yards for garbage disposal as land filling would also create enormous pollution and health hazards. The municipal authorities find it expensive to transport and dispose it of scientifically.
The Department of Science & Technology (DST) in collaboration with CMC Limited, initiated a pilot project on Integrated Waste Management (IWM) in Mumbai. The project offers a technological solution for disposal of city garbage and provides an option for making environmentally cleaner metropolis. After going through several technology options and assessing marketability of the product, IWM project opted for pelletisation technology over other processes like incineration, bio-gas and compost production, for dealing with this issue scientifically. Over two years of dedicated efforts, involving a great deal of developmental work, have resulted in the establishment of a technology for pelletising the combustibles separated from the municipal garbage.
A prototype fuel pelletisation plant was engineered and erected at Deonar, Mumbai. The production process has been established at the rate of 2 TPH with fuel pellets of high calorific value, which find easy acceptability to industries such as thermal power plants (for boilers with fixed grate, travelling grate, fluidised bed), multi-fuel package boilers for process steam, foundries, restaurants etc.
The process involves primarily, solar drying, separation of incombustible, size reduction and pelletisation, as shown in the following block diagram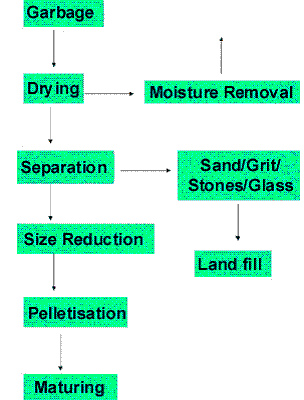
The fuel pellets so produced, are of cylindrical shape catering to a wide variety of end uses. These are hard enough to be transported loose and can be stored like coal.
Characteristics of Fuel Pellets
| Size | Dia : 8/20/30 mm, length : 8-40 mm |
| Calorific Value | 3500 Kcal/Kg. |
| Bulk Density | 0.7 MT per cu. M. |
| Density | 1.3 gms./cc |
| Ash Content | < 15 % |
| Moisture | 10 % (approx.) |
The fuel pellets have several distinct advantages over coal/wood like
- Cleaner fuel, free from incombustiles
- Lower ash content
- Low moisture content
- Uniform size
- Eco-friendly
- Regular, trouble free supply and
- Cost-effective
This technology, demonstrated by DST & CMC to produce fuel pellets, is available for commercial exploitation through Technology Information, Forecasting and Assessment Council , an autonomous organization under DST. The plant offered here, an economically viable one, is engineered with indigenous equipment. The plant design would have to be tailored in accordance with the quality and quantity of garbage available in a city.
Plant Highlights
| Capacity | 100 TPD fuel pellets |
| Raw garbage input | 400-500 TPD |
| Connected load | 600 HP |
| Land | 2-4 acres |
| Working hours per day | 20 |
| Working days per year | 250 |
The problem of coal in respect of availability, quality, higher prices etc. can be overcome by using fuel pellets. A number of such plants are currently operating in USA, UK etc. Various grades of fuel pellets have been test marketed at different industries in India to establish the marketability. These are economical and have tremendous market potential in our country.
Learning from above pilot project, TIFAC and CMC have now embarked on the design & installation of a 1000 TPD fuel pelletisation plant from municipal garbage in Hyderabad.
A comprehensive technology transfer package encompassing the following is available:
- Project feasibility report
- Plant design and project report
- Tendering, Vendor selection, procurement and inspection support
- Plant installation and commissioning
- Training for operation, maintenance and marketing
For further information please contact
Please contact Mr. S. Biswas
Email: biswas@alpha.nic.in







